4.4. Administrative Controls
When administering a home machine, the user has to perform some tasks as the root user or by acquiring effective root privileges via a setuid program, such as sudo or su. A setuid program is one that operates with the user ID (UID) of the owner of program rather than the user operating the program. Such programs are denoted by a lower case s in the owner section of a long format listing.
For the system administrators of an organization, however, choices must be made as to how much administrative access users within the organization should have to their machine. Through a PAM module called pam_console.so, some activities normally reserved only for the root user, such as rebooting and mounting removable media are allowed for the first user that logs in at the physical console (see the chapter titled Pluggable Authentication Modules (PAM) in the Red Hat Linux Reference Guide for more about the pam_console.so module). However, other important system administration tasks such as altering network settings, configuring a new mouse, or mounting network devices are impossible without administrative access. As a result system administrators must decide how much administrative access the users on their network should receive.
4.4.1. Allowing Root Access
If the users within an organization are a trusted, computer-savvy group, then allowing them root access may not be a bad thing. Allowing root access by users means that minor issues like adding devices or configuring network interfaces can be handled by the individual users, leaving system administrators free to deal with network security and other important issues.
On the other hand, giving root access to individual users can lead to the following issues (to name a few):
Machine Misconfiguration — Users with root access can misconfigure their machines and require assistance or worse, open up security holes without knowing it.
Run Insecure Services — Users with root access may run insecure servers on their machine, such as FTP or Telnet, potentially putting usernames and passwords at risk as they pass over the network in the clear.
Running Email Attachments As Root — Although rare, email viruses that effect Linux do exist. The only time they are a threat, however, is when they are run by the root user.
4.4.2. Disallowing Root Access
If an administrator is uncomfortable allowing users to log in as root for these or other reasons, the root password should be kept secret and access to runlevel one or single user mode should be disallowed through boot loader password protection (see Section 4.2.2 Boot Loader Passwords for more on this topic).
Table 4-1 shows ways an administrator can further ensure that root logins are disallowed:
| Method | Description | Effects | Does Not Effect | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Changing the root shell. | Edit the /etc/passwd file and change the shell from /bin/bash to /sbin/nologin. |
|
| |||||||||||||||
| Disabling root access via any console device (tty). | An empty /etc/securetty file prevents root login on any devices attached to the computer. |
|
| |||||||||||||||
| Disabling root SSH logins. | Edit the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file and set the PermitRootLogin parameter to no. |
|
| |||||||||||||||
| Use PAM to limit root access to services. | Edit the file for the target service in the /etc/pam.d/ directory. Make sure the pam_listfile.so is required for authentication. See Section 4.4.2.4 Disabling Root Using PAM for details. |
|
|
Table 4-1. Methods of Disabling the Root Account
4.4.2.1. Disabling the Root Shell
To prevent users from logging in directly as root, the system administrator can set the root account's shell to /sbin/nologin in the /etc/passwd file. This will prevent access to the root account through commands that require a shell, such as the su and the ssh commands.
 | Important |
|---|---|
Programs that do not require access to the shell, such as email clients or the sudo command, can still access the root account. |
4.4.2.2. Disabling Root Logins
To further limit access to the root account, administrators can disable root logins at the console by editing the /etc/securetty file. This file lists all devices the root user is allowed to log into. If the file does not exist at all, the root user can log in through any communication device on the system, whether it by via the console or a raw network interface. This is dangerous because a user can Telnet into his machine as root, sending his password in plain text over the network. By default, Red Hat Linux's /etc/securetty file only allows the root user to log at the console physically attached to the machine. To prevent root from logging in, remove the contents of this file by typing the following command:
echo > /etc/securetty |
 | Warning |
|---|---|
A blank /etc/securetty file does not prevent the root user from logging in remotely using the OpenSSH suite of tools because the console is not opened until after authentication. |
4.4.2.3. Disabling Root SSH Logins
To prevent root logins via the SSH protocol, edit the SSH daemon's configuration file: /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Change the line that says:
# PermitRootLogin yes |
To read as follows:
PermitRootLogin no |
4.4.2.4. Disabling Root Using PAM
PAM, through the /lib/security/pam_listfile.so module, allows great flexibility in denying specific accounts. This allows the administrator to point the module at a list of users who are not allowed to log in. Below is an example of how the module is used for the vsftpd FTP server in the /etc/pam.d/vsftpd PAM configuration file (the \ character at the end of the first line in the following example is not necessary if the directive is on one line):
auth required /lib/security/pam_listfile.so item=user \ sense=deny file=/etc/vsftpd.ftpusers onerr=succeed |
This tells PAM to consult the file /etc/vsftpd.ftpusers and denying any user listed access to the service. The administrator is free to change the name of this file and can keep separate lists for each service or use one central list to deny access to multiple services.
If the administrator wants to deny access to multiple services, a similar line can be added to the PAM configuration services, such as /etc/pam.d/pop and /etc/pam.d/imap for mail clients or /etc/pam.d/ssh for SSH clients.
For more information about PAM, see the chapter titled Pluggable Authentication Modules (PAM) in the Red Hat Linux Reference Guide.
4.4.3. Limiting Root Access
Rather than completely deny access to the root user, the administrator may wish to allow access only via setuid programs, such as su or sudo.
4.4.3.1. The su Command
Upon typing the su command, the user is prompted for the root password and, after authentication, given a root shell prompt.
Once logged in via the su command, the user is the root user and has absolute administrative access to the system. In addition, once a user has attained root, it is possible in some cases for them to use the su command to change to any other user on the system without being prompted for a password.
Because this program is so powerful, administrators within an organization may wish to limit who has access to the command.
One of the simplest ways to do this is to add users to the special administrative group called wheel. To do this, type the following command as root:
usermod -G wheel <username> |
In the previous command, replace <username> with the username being added to the wheel group.
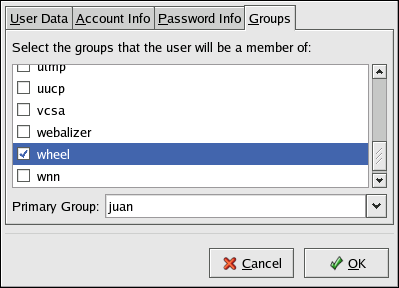
To use the User Manager for this purpose, go to the Main Menu Button (on the Panel) => System Settings => Users & Groups or type the command redhat-config-users at a shell prompt. Select the Users tab, select the user from the user list, and click Properties from the button menu (or choose File => Properties from the pull-down menu).
Then select the Groups tab and click on the wheel group, as shown in Figure 4-2.
Next open the PAM configuration file for su,
/etc/pam.d/su, in a text editor and remove the
comment
auth required /lib/security/pam_wheel.so use_uid |
Doing this will permit only members of the administrative group wheel to use the program.
 | Note |
|---|---|
The root user is part of the wheel group by default. |
4.4.3.2. The sudo Command
The sudo command offers another approach for giving users administrative access. When a trusted user precedes an administrative command with sudo, he is prompted for his password. Then, once authenticated and assuming that the command is permitted, the administrative command is executed as if by the root user.
The basic format of the sudo command is as follows:
sudo <command> |
In the above example, <command> would be replaced by a command normally reserved for the root user, such as mount.
 | Important |
|---|---|
Users of the sudo command should take extra care to log out before walking away from their machines since sudoers can use the command again without being asked for a password for a five minute period. This setting can be altered via the configuration file, /etc/sudoers. |
The sudo command allows for a high degree of flexibility. For instance, only users listed in the /etc/sudoers configuration file are allowed to use the sudo command and the command is executed in the user's shell, not a root shell. This means the root shell can be completely disabled, as shown in Section 4.4.2.1 Disabling the Root Shell.
The sudo command also provides a comprehensive audit trail. Each successful authentication is logged to the file /var/log/messages and the command issued along with the issuer's user name is logged to the file /var/log/secure.
Another advantage of the sudo command is that an administrator can allow different users access to specific commands based on their needs.
Administrators wanting to edit the sudo configuration file, /etc/sudoers, should use the visudo command.
To give someone full administrative privileges, type visudo and add a line similar to the following in the user privilege specification section:
juan ALL=(ALL) ALL |
This example states that the user, juan, can use sudo from any host and execute any command.
The example below illustrates the granularity possible when configuring sudo:
%users localhost=/sbin/shutdown -h now |
This example states that any user can issue the command /sbin/shutdown -h now as long as it is issued from the console.
The man page for sudoers has a detailed listing of options for this file.