14.3. Services Configuration Tool
The Services Configuration Tool is a graphical application developed by Red Hat to configure which SysV services in the /etc/rc.d/init.d directory are started at boot time (for runlevels 3, 4, and 5) and which xinetd services are enabled. It also allows you to start, stop, and restart SysV services as well as restart xinetd.
To start the Services Configuration Tool from the desktop, go to the Main Menu Button (on the Panel) => System Settings => Server Settings => Services or type the command redhat-config-services at a shell prompt (for example, in an XTerm or a GNOME terminal).
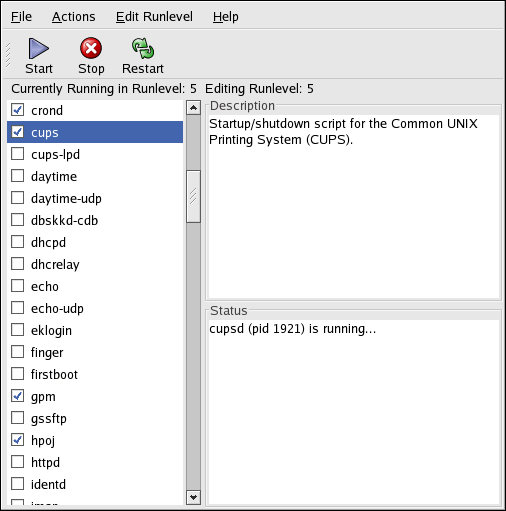
The Services Configuration Tool displays the current runlevel as well as the runlevel you are currently editing. To edit a different runlevel, select Edit Runlevel from the pulldown menu and select runlevel 3, 4, or 5. Refer to Section 14.1 Runlevels for a description of runlevels.
The Services Configuration Tool lists the services from the /etc/rc.d/init.d directory as well as the services controlled by xinetd. Click on the name of the service from the list on the left-hand side of the application to display a brief description of that service as well as the status of the service. If the service is not an xinetd service, the status window shows whether or not the service is currently running. If the service is controlled by xinetd, the status window displays the phrase xinetd service.
To start, stop, or restart a service immediately, select the service from the list and click the appropriate button on the toolbar (or choose the action from the Actions pulldown menu). If the service is an xinetd service, the action buttons are disabled because they can not be started or stopped individually.
If you enable/disable an xinetd service by checking or unchecking the checkbox next to the service name, you must select File => Save Changes from the pulldown menu to restart xinetd and immediately enable/disable the xinetd service that you changed. xinetd is also configured to remember the setting. You can enable/disable more than one xinetd service at a time and save the changes when you are finished.
For example, assume you check rsync to enable it in runlevel 3 and then save the changes. The rsync service is immediately enabled. The next time xinetd is started, rsync is still enabled.
 | Warning |
|---|---|
When you save changes to xinetd services, xinetd is restarted, and the changes take place immediately. When you save changes to other services, the runlevel is reconfigured, but the changes do not take effect immediately. |
To enable a non-xinetd service to start at boot time for the currently selected runlevel, check the checkbox beside the name of the service in the list. After configuring the runlevel, apply the changes by selecting File => Save Changes from the pulldown menu. The runlevel configuration is changed, but the runlevel is not restarted; thus, the changes do not take place immediately.
For example, assume you are configuring runlevel 3. If you change the value for the anacron service from checked to unchecked and then select Save Changes, the runlevel 3 configuration changes so that anacron is not started at boot time. However, runlevel 3 is not reinitialized, so anacron is still running. Select one of following options at this point:
Stop the anacron service — Stop the service by selecting it from the list and clicking the Stop button. A message will be displayed stating that the service was stopped successfully.
Reinitialize the runlevel — Reinitialize the runlevel by going to a shell prompt and typing the command telinit 3 (where 3 is the runlevel number). This option is recommended if you change the Start at Boot value of more than one service and want to activate the changes immediately.
Do nothing else — You do not have to stop the anacron service. You can wait until the system is rebooted for the service to stop. The next time the system is booted, the runlevel will be initialized without the anacron service running.